One of the key requirements for modern UI is being performant. No matter how beautiful your app looks and what killer features it offers, it will frustrate your users if it clangs.
React performance optimization is a pretty well-covered topic. If you'd like more information on this,, Fix the slow render before you fix the re-render might be a good starting point. But is there a guarantee these optimizations will last? If not careful, it takes one unstable prop to force the entire app re-render and introduce lags noticeable to the user. Of course, this can be handled by manual testing, but it makes sense to look for some kind of automated solution.
Our experience with Jest
We had this problem at our latest project. This affected a pretty complex application that should be highly responsive to user input. Sometimes an unstable prop would sneak in and force re-render of a large DOM chunk. It was always easy to make it fast again, but we wanted to avoid this in the future. So, we looked for a way to automatically check for changes that affected rendering.
The first step was to understand exactly what metrics we want to catch. Of course, it was tempting to measure something that would matter to the end user. Something like render time would do, but this metric is very fuzzy – so we decided to go with something like the number of renders. This is not ideal, but these tests would be idempotent and independent of their environment. This is also somewhat contrary to the “fix slow renders, not re-renders” philosophy, but it still has a good thing – it helps us catch mistakes without manually re-testing a bunch of cases.
Now for the implementation. We don’t need real DOM for counting re-renders, so we decided to go with Jest. In order to interact with React internals and count re-renders, we used Profiler component. It is basically just a component that accepts children and onRender callback.
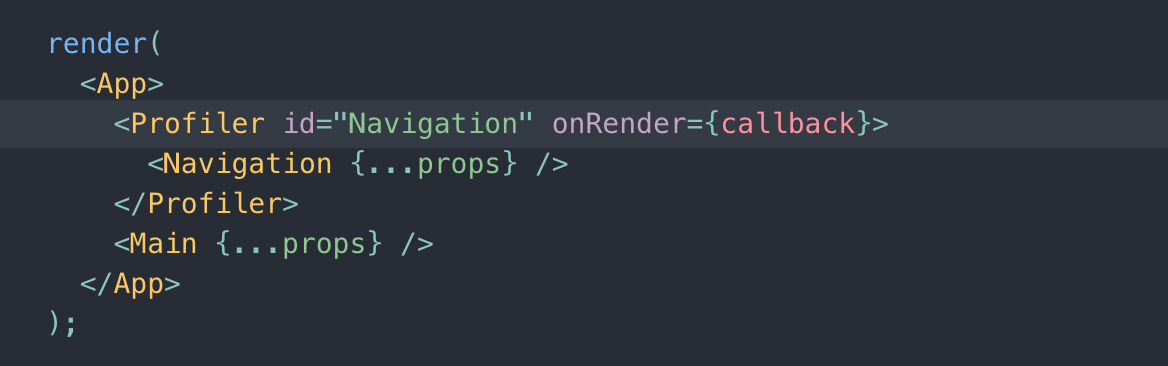
Technically, this is already enough to count renders. But we wanted to make profiler really easy to use, so we created a Higher-Order Component:
const withProfiler = (Component, id: string = 'rootComponent') => {
const componentId = `withProfiler${id}`;
const onRender = () => {
SnapshotProfiler.__numRenders++;
};
const SnapshotProfiler = React.memo((props) => {
return (
);
});
SnapshotProfiler.__numRenders = 0;
SnapshotProfiler.clearCounters = function () {
this.__numRenders = 0;
};
return SnapshotProfiler;
};
const Foo = () => (Foo)
const DecoratedFoo = withProfiler(Foo);
Now we can just wrap any component with this HOC, and we can access the number of times that component has been rendered. Rendering DecoratedFoo will effectively render Foo, but will also store a __numRenders counter. And since it is stored inside the component object, rendering any instance of this component will increase the counter. So, if we render the following jsx:
we will have DecoratedFoo.__numRenders === 2 .
This is all well and good, but it's still a little awkward to have withProfiler HOC to components used in a real app. Fortunately, Jest has flexible tools for mocking, so we could make great use of them.
Let’s say we have a ChessBoard component that renders 64 instances of Square component. On each move it should typically re-render 2 more cells, since a single chess piece moves from square to square. So we can create the following mock setup and write the following tests:
jest.mock("./Square", () => ({
Square: jest
.requireActual("../profiler")
.withProfiler(jest.requireActual("./Square").Square),
}));
describe("Chess performance test", () => {
function clearCounters() {
Square.clearCounters();
}
beforeEach(() => {
clearCounters();
});
const initialSquareRendersCount = 64;
test("initial render", () => {
render();
expect(Square.__numRenders).toBe(initialCellRendersCount);
});
test("piece moving", () => {
const { rerender } = render( This way we can be sure the chessboard elements are rendered as many times as we need. So if someone accidentally puts a global state in every cell and the entire board will unnecessarily re-render - we will find out.
What we’ve done here is mocked Square, so in tests we have the same component wrapped into withProfiler HOC. Thus, the tests themselves do not alter the component structure, and are rendered just like in a regular environment. The code of the component itself does not change too. So, if we have a complex hierarchy of components and some really specific actions causing too many re-renders of a particular component, we can test just that.
I hope this helps you write more performant web applications. Good luck!






